Posterior Impingement Syndrome Elbow
Posterior impingement syndrome elbow. Activity that involves forceful elbow extension can cause triceps tendinosis or posterior impingement syndrome. Posterior impingement of the elbow joint usually occurs due to repeated extension of the elbow. 1 windup 2 early cocking 3 late cocking 4 acceleration 5 deceleration and 6 follow-through.
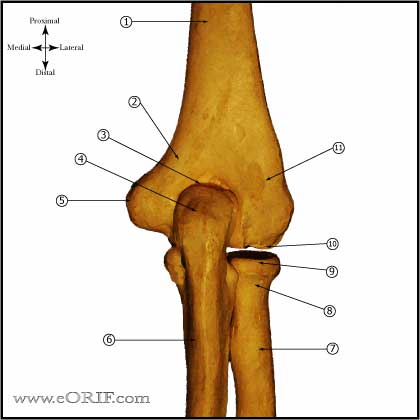
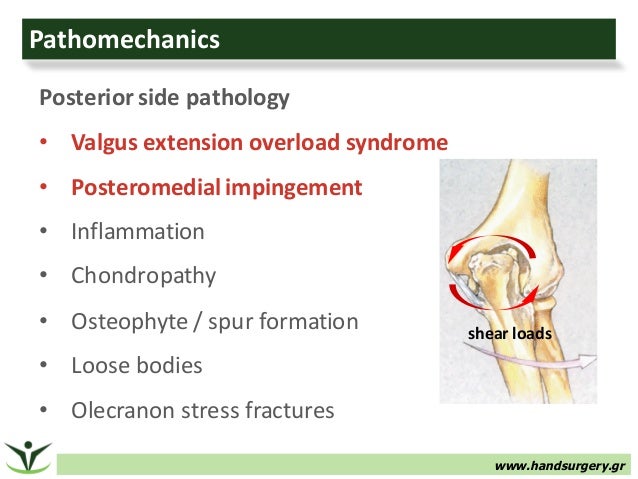
The radial nerve divides into two branches at the elbow. This may occur at several locations in the elbow and upper forearm. Posteromedial elbow impingement is a source of disability in the overhead throwing athlete.
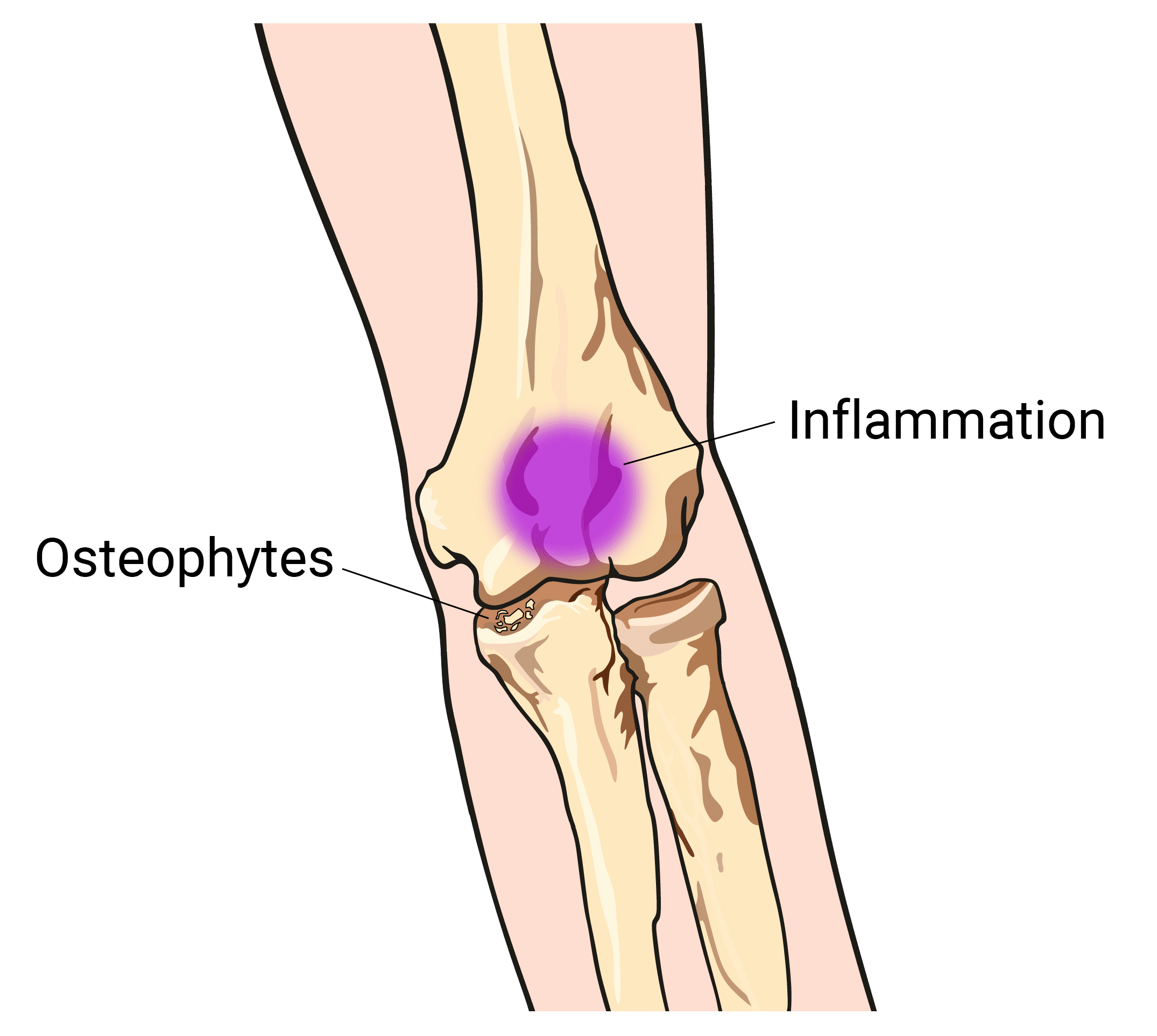
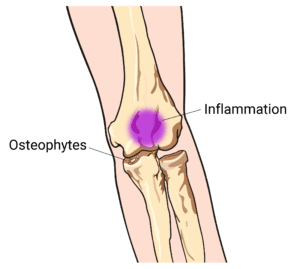
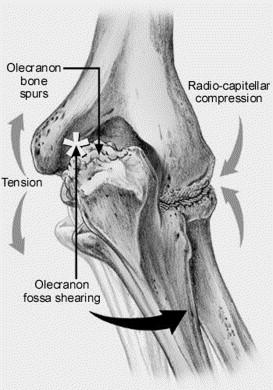
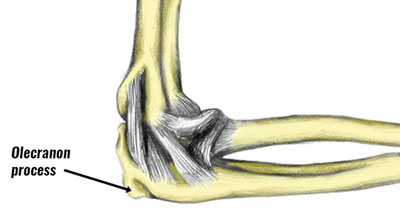
This syndrome may lead to the development of bone spurs extra bone that forms on the edge of an existing bone and inability to extend the elbow. Posterior Elbow Pain Swelling Catching andor Locking Phase of Throwing. These are the superficial radial nerve and the posterior interosseous nerve PI nerve.
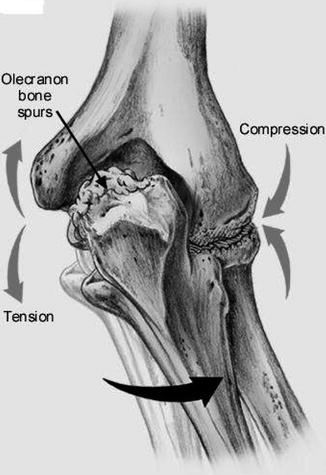
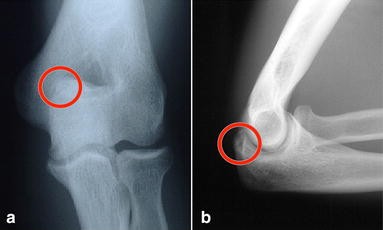
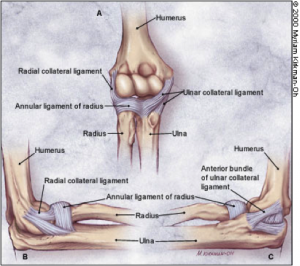
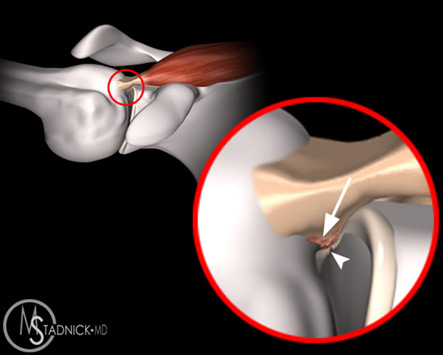
Olecranon impingement within the olecranon fossa. In addition any activity that causes increased valgus stress on the elbow can also cause posterior impingement syndrome or. Posterior Impingement of the Elbow Fig.
This may occur during sports such as overhead racket sports throwing swimming and boxing. Throwing javelin Older patients. It is the posterior interosseous nerve that may become entrapped or compressed.
Posteromedial Elbow Tests Posteromedial Impingement Test Elbow at 20º to 30º Valgus Stress Force Terminal Extension. Elbow impingement is a condition characterized by compression and damage to soft tissue such as cartilage situated at the back of or within the elbow joint. May stimulate the formation of osteophytes with chronic impingement.
Posterior impingement is due to over use and repetitive forced extensions of the elbow. Also known as Posterior Impingement Syndrome Posterior Impingement of the Elbow What is elbow impingement.
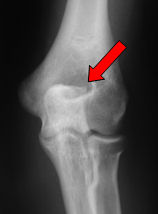
This study indicates that MRI identifies a reproducible pattern of pathology in.
These are the superficial radial nerve and the posterior interosseous nerve PI nerve. May stimulate the formation of osteophytes with chronic impingement. This may occur during sports such as overhead racket sports throwing swimming and boxing. Olecranon impingement within the olecranon fossa. Can cause biceps tendinosis or anterior capsule strain. This syndrome may lead to the development of bone spurs extra bone that forms on the edge of an existing bone and inability to extend the elbow. Snapping Triceps Syndrome. Posteromedial Elbow Tests Posteromedial Impingement Test Elbow at 20º to 30º Valgus Stress Force Terminal Extension. Activity that involves forceful elbow extension can cause triceps tendinosis or posterior impingement syndrome.
These are the superficial radial nerve and the posterior interosseous nerve PI nerve. Olecranon impingement within the olecranon fossa. Posteromedial Elbow Tests Posteromedial Impingement Test Elbow at 20º to 30º Valgus Stress Force Terminal Extension. Posterior impingement of the elbow joint usually occurs due to repeated extension of the elbow. In addition any activity that causes increased valgus stress on the elbow can also cause posterior impingement syndrome or. Can cause biceps tendinosis or anterior capsule strain. This study indicates that MRI identifies a reproducible pattern of pathology in.

























Post a Comment for "Posterior Impingement Syndrome Elbow"