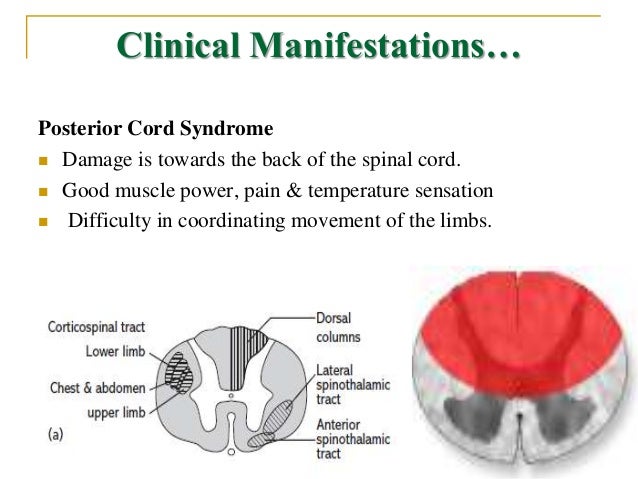
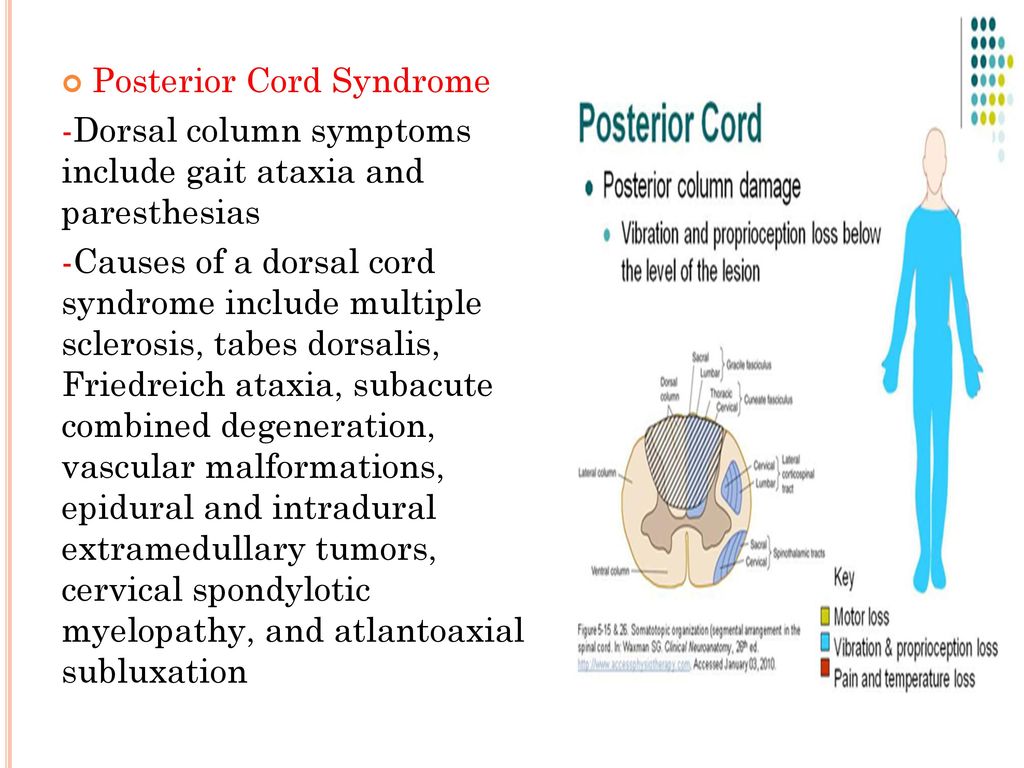
Posterior Cord Syndrome Symptoms
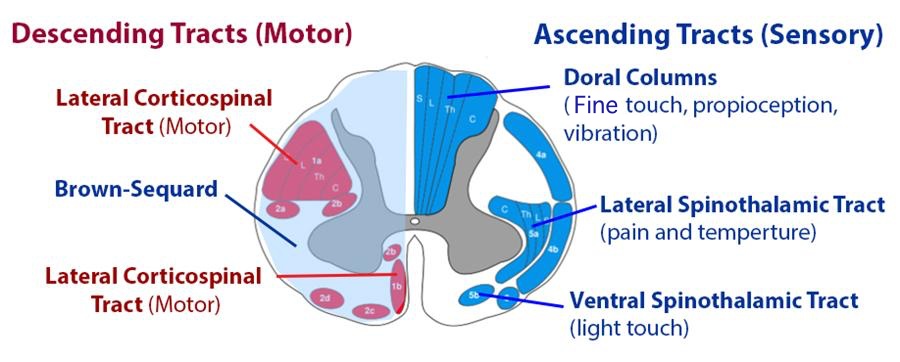
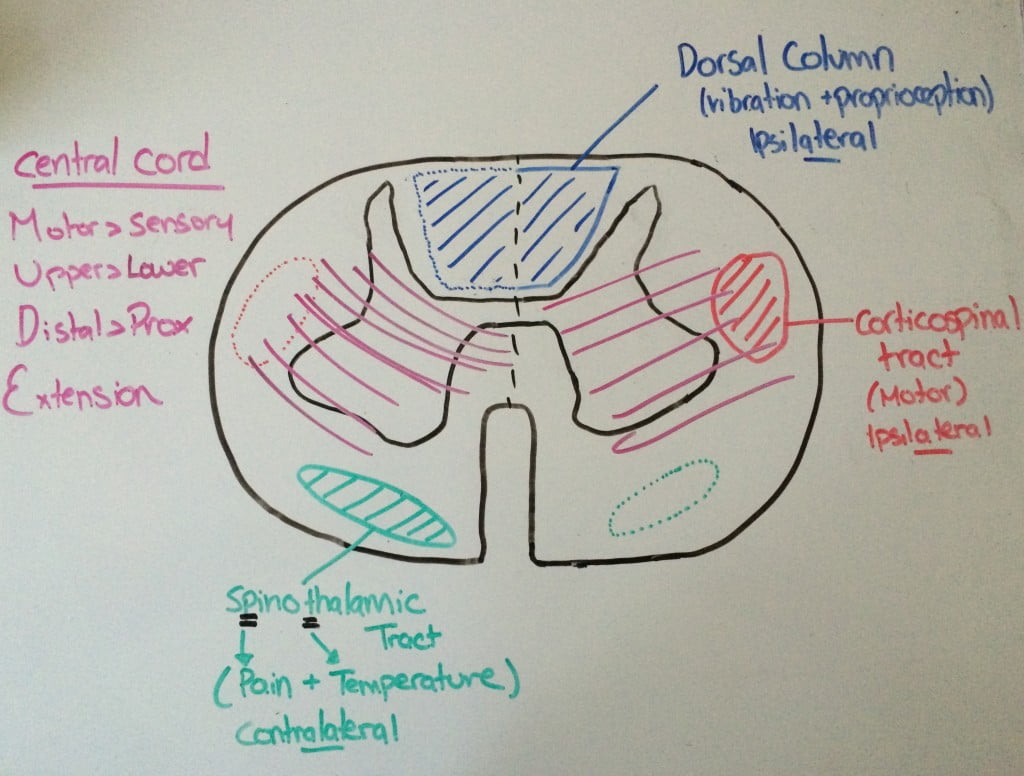
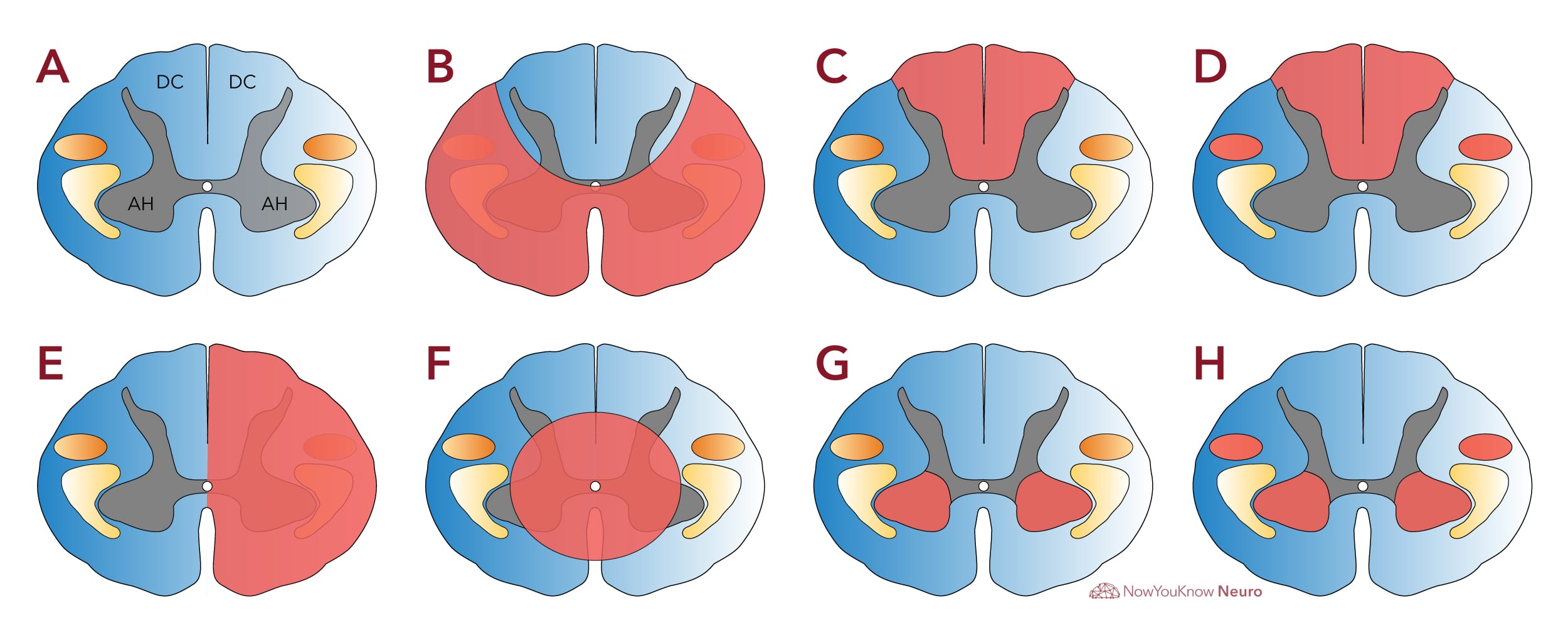
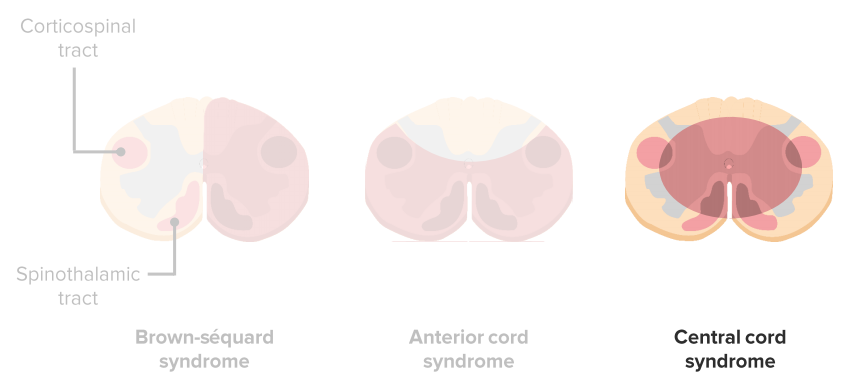
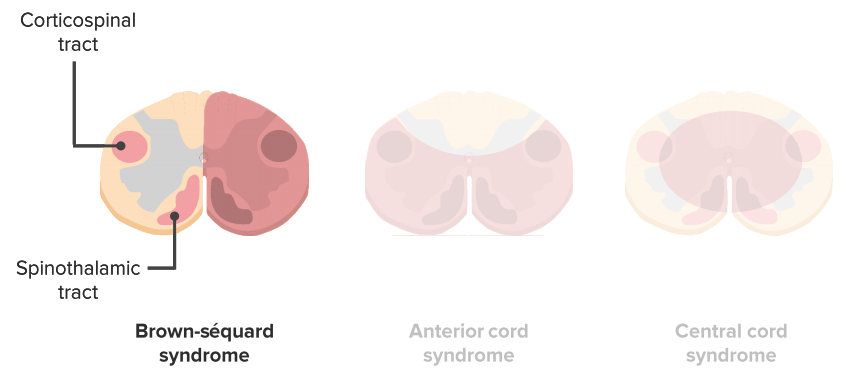
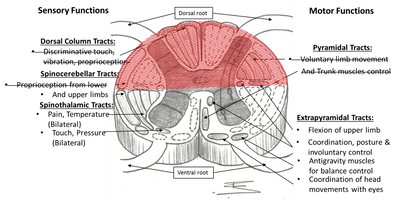
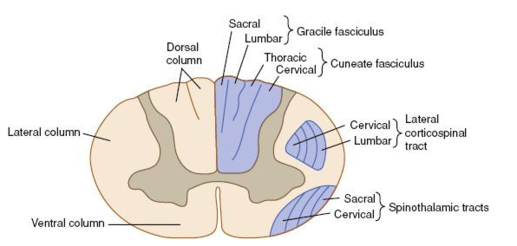
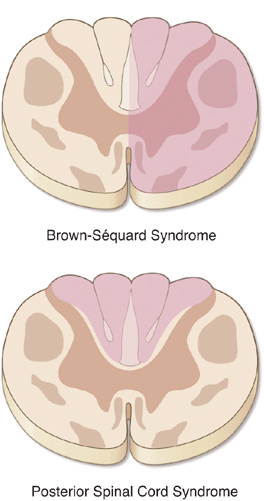
Posterior cord syndrome symptoms. And in severe circumstances complete paralysis below the portion of the spinal cord affected. Bilateral loss of proprioception vibration and touch sensation below the level of the lesion 4 Brown-Séquard syndrome hemisection syndrome Hemisection of the cord. Findings of posterior cord syndrome include loss of proprioception and vibration which are not routinely tested with the American Spinal Cord Injury Associations International Standards for Neurological Classification of Spinal Cord Injury ISNCSCI exam and can easily be missed.
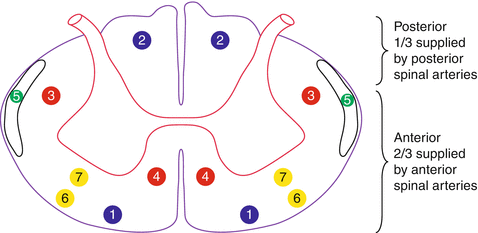
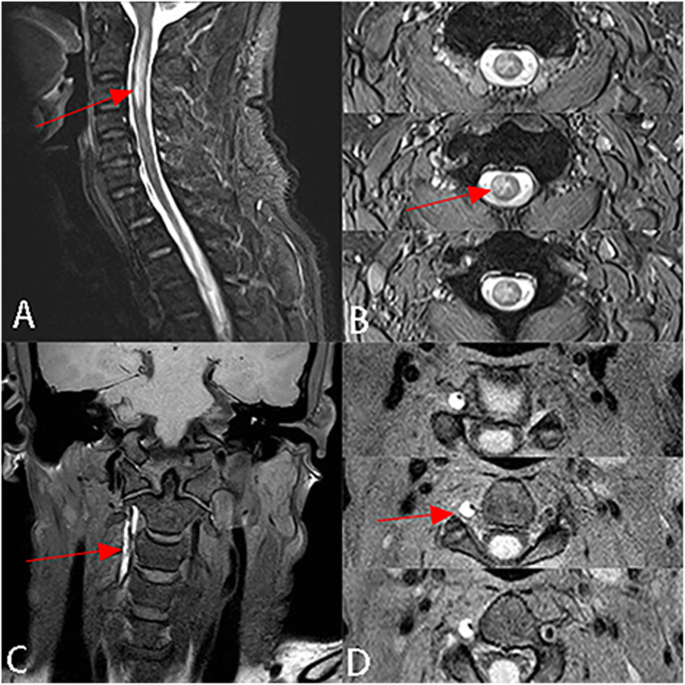
Trauma eg penetrating injury Occlusion of the posterior spinal artery. B Sagittal contrast-enhanced MR image shows an intensely enhancing expansile mass large white arrow with a focal hypointense. Signal arrowhead secondary to hemorrhage and polar cysts small white arrows.
Posterior Cord Injury Symptoms Individuals with posterior cord syndrome experience impaired sensation below the site of injury. Posterior cord syndrome is a rare type of incomplete spinal cord injury that affects the dorsal or posterior columns of the spinal cord which are responsible for the perception of vibration fine-touch and body positioning ie. Anterior Cord Syndrome Atlantoaxial Instability Atlantoaxial Rotary Fixation Brachial Plexus Burner Central Cord Syndrome Cervical Disc Disease Cervical Disc Herniation Rehabilitation Cervical Ligamentous Instability Cervical Neck Strain Cervical Spinal Stenosis Cervical Spine Fracture Cervical Spine Injury Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy Complete Cord Syndrome Posterior Cord Syndrome Spinal Cord Hemisection Spinal Cord Syndrome.
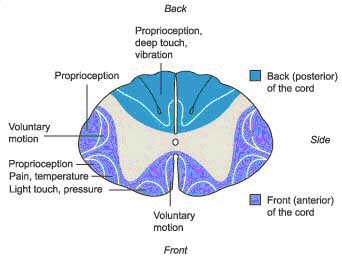
The PCS is accompanied by a positive Romberg sign tingling in the affected regions sensory ataxia hypotonia and preserved pain and temperature sense. Progressive sensory and motor deficits may affect the legs potentially resulting in numbness weakness or. These patients have preserved function of their posterior column and so their proprioception and vibration sense is intact.
This weakness may result in difficulty with every-day tasks such as doing up buttons writing or even walking. Moreover general symptoms of posterior spinal artery infarcts include ipsilateral loss of proprioceptive sensation fine touch pressure and vibration below the lesion. Intermittent syncope Drop attacks Vertigo Confusion or altered consciousness Weakness Visual disturbance.
Posterior Cord syndrome is one of the type of incomplete sp. This presentation is very rare and individuals will display profound ataxia due to loss of proprioception. Posterior Cord syndrome is defined as injury in posterior artery of spinal cord.
Symptoms common to adult tethered cord syndrome include constant often severe back and leg pain which may extend to the rectum and genital area in some cases. People with posterior cord syndrome can present with poor balance unsteady walking and frequent falls which typically worsen in dark environments.
Posterior Cord Injury Symptoms Individuals with posterior cord syndrome experience impaired sensation below the site of injury.
This weakness may result in difficulty with every-day tasks such as doing up buttons writing or even walking. Patients may also note a lack of sensation and difficulty urinating. The PCS is accompanied by a positive Romberg sign tingling in the affected regions sensory ataxia hypotonia and preserved pain and temperature sense. Anterior Cord Syndrome Atlantoaxial Instability Atlantoaxial Rotary Fixation Brachial Plexus Burner Central Cord Syndrome Cervical Disc Disease Cervical Disc Herniation Rehabilitation Cervical Ligamentous Instability Cervical Neck Strain Cervical Spinal Stenosis Cervical Spine Fracture Cervical Spine Injury Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy Complete Cord Syndrome Posterior Cord Syndrome Spinal Cord Hemisection Spinal Cord Syndrome. This presentation is very rare and individuals will display profound ataxia due to loss of proprioception. Posterior cord syndrome is a rare type of incomplete spinal cord injury that affects the dorsal or posterior columns of the spinal cord which are responsible for the perception of vibration fine-touch and body positioning ie. Posterior cord syndrome. And in severe circumstances complete paralysis below the portion of the spinal cord affected. This weakness may result in difficulty with every-day tasks such as doing up buttons writing or even walking.
Bilateral loss of proprioception vibration and touch sensation below the level of the lesion 4 Brown-Séquard syndrome hemisection syndrome Hemisection of the cord. Posterior cord syndrome Posterior column syndrome Neurology A condition due to the loss of vibration and position sense below a lesion of the posterior spinal cord. Being that the fibers have not crossed yet the patient will experience isolated ipsilateral loss of two point discrimination vibration and conscious proprioception. Moreover general symptoms of posterior spinal artery infarcts include ipsilateral loss of proprioceptive sensation fine touch pressure and vibration below the lesion. Clinicians should suspect PRES-SCI when patients with PRES have neurologic signs referable to the spinal cord extreme elevation in blood pressure MRI lesions that extend to the cervicomedullary junction or grade IV hypertensive retinopathy. Posterior cord syndrome is a rare type of incomplete spinal cord injury that affects the dorsal or posterior columns of the spinal cord which are responsible for the perception of vibration fine-touch and body positioning ie. Progressive sensory and motor deficits may affect the legs potentially resulting in numbness weakness or.































Post a Comment for "Posterior Cord Syndrome Symptoms"